Why Does My Ear Hurt?
It’s a universal human experience where something will start aching, and you can’t tell whether your body is just having a bad day or if it could be something serious. While earaches are often not a cause for serious concern, they can sometimes indicate underlying health issues that require medical attention.
Causes of Ear Pain
1.Earwax Buildup
Earwax, or cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the glands in the ear canal. Its purpose is to protect the ear from dust, foreign particles, and microorganisms. However, excessive earwax can accumulate and harden, leading to discomfort and pain.
- Symptoms: You may experience a feeling of fullness in the ear, diminished hearing, and sometimes a ringing sound.
- Earache Treatment: Earwax can often be managed at home with over-the-counter ear drops designed to soften the wax. In some cases, a healthcare professional may need to remove the buildup using specialised tools.
2.Ear Infection
Ear infections are one of the most common causes of ear pain, particularly in children. They occur when bacteria or viruses infect the middle ear, often following a cold or respiratory infection.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include ear pain, fluid drainage, difficulty hearing, fever, and irritability in children.
- Earache Treatment: Mild ear infections may resolve on their own, but severe cases may require antibiotics. Pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage the pain and fever. However, we recommend seeing a specialist incase it gets worse.
3.Swimmer's Ear
Swimmer's ear, or otitis externa, is an infection of the outer ear canal caused by bacteria or fungi. It often occurs after swimming or exposure to water, which creates a moist environment ideal for bacterial growth.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include ear pain, itching, redness, and discharge from the ear.
- Earache Treatment: Treatment typically involves ear drops containing antibiotics or antifungal medication. Keeping the ear dry and avoiding water activities until the infection clears is also crucial.
4.Allergies
Allergies can cause inflammation and congestion in the ear, leading to pain and discomfort. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods.
- Symptoms: Symptoms may include ear pain, itching, nasal congestion, and sneezing.
- Earache Treatment: Managing allergies with antihistamines and decongestants and avoiding known allergens can help reduce ear pain. If you’re unsure of what might be causing the allergies, we recommend you get an allergy test.
5.Changes in Air Pressure
Rapid changes in air pressure, such as during aeroplane travel or scuba diving, can cause ear pain. This condition, known as barotrauma, occurs when the pressure in the middle ear is out of balance with the external pressure.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include ear pain, a feeling of fullness, and sometimes temporary hearing loss.
- Earache Treatment: Yawning, swallowing, or chewing gum can help equalise ear pressure. For more severe cases, decongestants or nasal sprays may be recommended before travel.
Ear Pain (Otalgia)
Ear pain, medically known as otalgia, can stem from various causes, the most common being infections of the external canal (otitis externa, furunculosis) or middle ear (otitis media). The nerves that provide sensation to the mouth, nose, and throat also supply the ear and the jaw (temporomandibular) joint. Therefore, pain may sometimes be referred to as the strain of the jaw joint with spasms of the adjacent chewing muscles or conditions affecting other ENT sites.
Diagnostics
When you experience persistent or severe ear pain, it is crucial to undergo proper diagnostic procedures to determine the cause and appropriate treatment. Here are some common diagnostic methods used to evaluate ear pain:
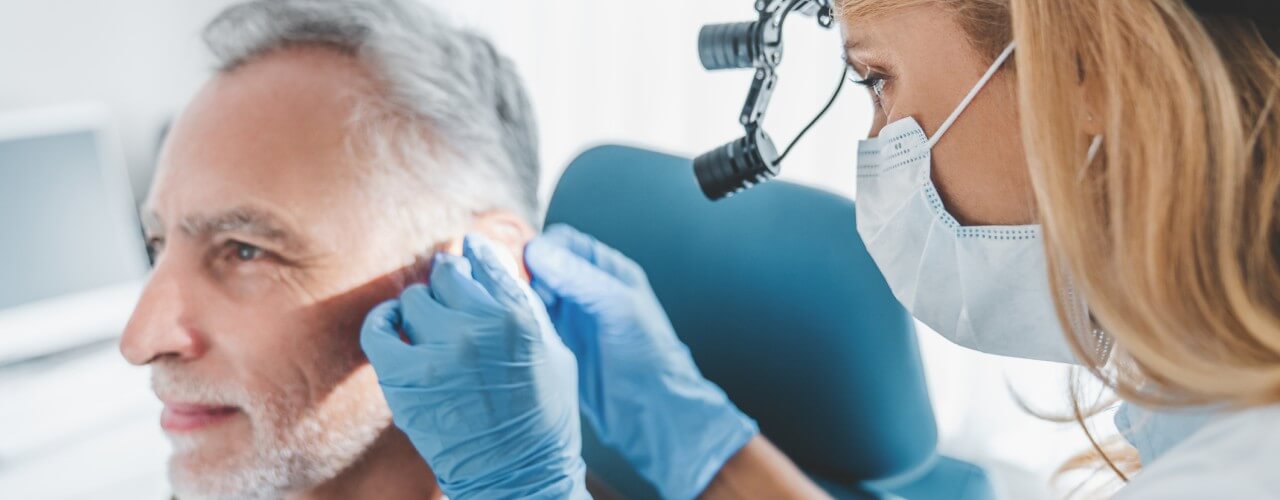
Microscopy
Microscopy involves a detailed examination of the external canal and eardrum using an operating microscope for magnification. Given that the normal eardrum is only about 1 cm in diameter, enlarging this by x4 or higher provides more accurate diagnostic information.
The examination chair is reclined to stabilise the patient's head, preventing even minor movements that could cause discomfort. A single-use sterile plastic speculum is introduced into the ear canal, and the overhead microscope is swung into position. This short procedure is painless.
Microsuction
Accumulated wax is often present in a normal ear canal and can prevent proper inspection of the skin lining the canal or eardrum. Excessive wax can cause hearing loss, affect the results of hearing tests, or interfere with other diagnostic procedures.
Wax is typically removed by inserting a small suction device through a sterile plastic speculum under a microscope, a process known as microsuction. This is normally a painless procedure. Although ear syringing with warm water has been used traditionally, it carries a risk of causing permanent damage to the ear, especially if there are underlying issues like a perforated eardrum.
Ear Swab for Microscopy and Culture
Bacterial or fungal infections require specific antimicrobial treatments. When an infection is suspected, a sample of pus, which may be thick, yellow-green, and have an unpleasant smell, is sent for laboratory analysis.
After inserting a sterile plastic speculum into the ear canal, a fine sterile cotton bud is used to collect a sample of the pus. This sample is stored in preservatives and sent to the laboratory, where a microbiologist examines it under a microscope to identify the infective organism. The organism is then cultured on a special gel, and various drugs are applied to determine the most effective antimicrobial treatment.
Pure Tone Audiometry
This is a basic subjective hearing test to determine your ability to hear various sounds at different frequencies.
You will sit in a soundproof booth with headphones and press a button each time you hear a beep sound, even if faint. Ignore any rushing sounds used to mask the opposite ear and only respond to the beeps. The test can take up to 20 minutes depending on the results.
Tympanometry
This objective test assesses middle ear function and helps determine the presence of fluid or congestion in the middle ear, perforations in the eardrum, weaknesses in the eardrum, discontinuity of the ossicles due to disease or trauma, blocked grommets, or fistulas in the bone surrounding the balance organ.
You will sit still while the audiologist holds a soft rubber probe at the entrance of your ear canal. You may feel a slight change of pressure in your ear during this test.
When to See a Doctor
It's important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or persistent ear pain
- Hearing loss
- Discharge or bleeding from the ear
- High fever
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Symptoms that worsen or do not improve with home treatment
Contact us or book an appointment to speak to one of our specialists.